Filter Tab
The Filter tab contains a spectral filter that allows you to shape the overall spectrum of the sound.
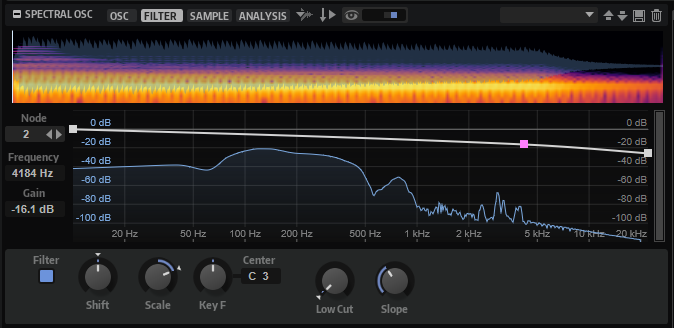
- Node
-
Displays the selected node. You can use the arrow buttons to switch between nodes.
- Frequency
-
Sets the frequency of the selected node.
- Gain
-
Sets the gain of the selected node.
- Filter On/Off
-
Activates/Deactivates the filter.
- Filter Shift
-
Allows you to shift the filter curve in the frequency domain. This is similar to shifting the cutoff frequency of a classic synthesis filter.
- Filter Scale
-
Scales the intensity of the Filter Shift.
With this parameter set to 0, Filter Shift and Filter Key Follow have no effect. With negative values, the effect of the Filter Shift settings is inverted.
- Filter Key Follow
-
Allows you to adjust the Filter Shift parameter with the notes you play.
Set this parameter to a positive value to raise the frequencies of the filter nodes with notes above the Center Key. Set it to a negative value to lower the frequencies of the filter nodes with notes above the Center Key.
At a setting of 100, a note that is played one octave above the Center Key doubles the frequencies of all filter nodes, and a note one octave below the Center Key halves the frequencies. This means that the filter curve follows the pitch of the played note.
- Center Key
-
Specifies the MIDI note that is used as the central position for the Key Follow function.
- Low Cut
-
Allows you to adjust the damping of low frequencies. The higher the amount, the more low frequencies are cut.
Low Cut does not work like a classic filter with a fixed cutoff frequency. Instead, it takes into account the current frequencies in the sample. For example, if you set this parameter to 10%, the low frequencies that occupy 10% of the overall energy in the spectrum are removed. This is especially useful to remove low rumbling sounds that can become audible when you apply pitch shift towards higher pitches. At higher values, Low Cut can produce more drastic effects.
- Slope
-
Allows you to set the slope of the filter, that is, to determine how fast frequencies within the low-cut range are attenuated.
Context Menu
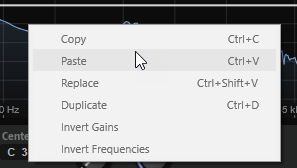
- Copy
-
Copies the selected nodes to the clipboard.
- Paste
-
Pastes the copied nodes at the insert position.
- Replace
-
Replaces the selected nodes with the nodes from the clipboard.
- Duplicate
-
Duplicates the selected nodes.
- Invert Gains
-
Flips the Gain values of the nodes around the vertical center of the selection. This way, you can turn a filter bump into a filter dip, for example.
- Invert Frequencies
-
Flips the nodes around the horizontal center of the selection. This way, you can mirror the symmetry of an asymmetrical filter shape, for example, to turn a low-pass filter into a high-pass filter.