Spectrum Tab
The Spectrum tab shows the amplitude and the phase spectrum of the extracted wave, that is, the amplitude and the phase for each harmonic.

The lowest harmonic is displayed on the left, the highest harmonic on the right.
The harmonics in the spectrum are represented by blue and orange bars. Blue bars represent the amplitude of the harmonics, that is, the magnitude spectrum. Orange bars represent the phase of the harmonics, that is, the phase spectrum. If the magnitude of a harmonic is zero, the corresponding phase is grayed out. You can obtain information on a particular harmonic by moving the mouse over its bar.
On the right, the frequency of the fundamental for each channel of the wave is displayed in Hz. This value is set automatically when a wave is extracted from a sample and represents the original pitch. If you created the spectrum manually, either by drawing or by inserting one of the basic waves from the Create New Wave menu, the value is set to 20 Hz. If no extracted pitch information is available, the fundamental allows you to determine which harmonic represents which frequency. For the default value of 20 Hz, the 1st harmonic is at 20 Hz, the second one at 40 Hz, the third one at 60 Hz, and so on. HALion provides 1024 harmonics, which means that you can create frequencies up to 20.480 Hz.
The number of editable harmonics in the spectrum view depends on the fundamental and on the setting of the Maximum Frequency parameter.
You can set the spectrums of a multi-channel wave for each individual channel or for all channels.
Toolbar

- Draw Tool
-

Allows you to change the spectrum by drawing with the mouse. The resulting wave is displayed on the right.
-
To draw in the magnitude or the phase spectrum, click in the display, and drag.
-
To draw a line, hold down Alt/Opt, and drag.
-
To adjust a single harmonic, click it, hold down Shift, and drag up/down.
-
To set the magnitude or the phase of a harmonic to zero, Ctrl/Cmd-click it.
To set the magnitude or phase of all harmonics to zero, hold down Shift-Ctrl/Cmd, and click.
NoteThe setting of the Phase Mode determines the impact of the Draw.
-
If you activate Keep Original Phases, only the focused wave is affected.
-
If you activate Align Phases and adjust the phase of the focused wave, the subsequent waves are also affected.
-
If you activate Reset Phases to Zero, you cannot adjust the phase spectrum with this tool.
-
- Selection Tool
-

Allows you to create range selections in the magnitude spectrum.
-
Drag the tool to make a selection. To select multiple channels of a multi-channel wave, drag the tool across the channels that you want to edit. Click the channel selector on the left to set the focus on a particular channel.
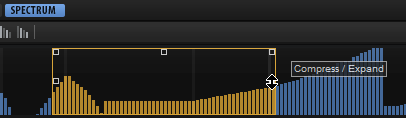
After making a selection, you can use the handles of the rectangle to perform the following editing functions:
-
To tilt the left part of the harmonic curve, use the handle in the top left corner. This allows you to tilt the harmonics at the start of the selection upwards or downwards.
Press Ctrl/Cmd to tilt the harmonics using a shelving filter curve instead of the linear curve.
-
To tilt the right part of the harmonic curve, use the handle in the top right corner. This allows you to tilt the harmonics at the end of the selection upwards or downwards.
Press Ctrl/Cmd to tilt the harmonics using a shelving filter curve instead of the linear curve.
-
To scale the harmonics, use the handle in the center of the top border. This allows you to raise or lower the harmonic values of the curve in percent.
Press Ctrl/Cmd to scale the harmonics with a bell curve.
Press Shift to offset the harmonics.
-
To scale the harmonics around their relative center, use the handle in the middle of the left and right borders. This allows you to raise or lower the harmonic values horizontally around the center of the selection.
-
To select all harmonics of the same pitch in all octaves that are higher than the current octave, double-click a harmonic.
NoteThis automatically switches to All Harmonics mode.
-
- Harmonics
-

With the Harmonics buttons, you can choose whether to edit all harmonics or to apply your editing exclusively to even or to odd harmonics.
-
Select All Harmonics
 to edit all harmonics.
to edit all harmonics. -
Select Odd Harmonics
 to edit only the odd-numbered harmonics.
to edit only the odd-numbered harmonics. -
Select Even Harmonics
 to edit only the even-numbered harmonics.
to edit only the even-numbered harmonics.
-
- Level in dB
-

If this button is activated, you can set the level in dB.
If this button is deactivated, you can adjust the level from minimum to maximum within a range of 0 to 100%.
- Linear/Logarithmic Frequency Display
-
Allows you to switch between a linear and a logarithmic frequency display.
The logarithmic frequency display takes up less space for showing the entire frequency range than the linear frequency display. It is useful for editing a range of harmonics with the Selection tool. For individual adjustments to the higher harmonics, we recommend to use the linear frequency display.
- Zoom
-
Allows you to choose from six predefined zoom factors.
- Channel Configuration
-

Wavetable synthesis in HALion supports multi-channel formats up to 5.1, which means that the wavetables can contain spectrums of up to 6 channels for each wave. The Channel Configuration parameter allows you to change the channel configuration of the waves.
Reducing the width results in unused channels, while expanding the width adds empty channels. For example, if you set the configuration of a stereo wave to mono, only the left channel is used.
Changing this parameter alters how the channels are assigned to the six internal bus channels. For example, Quadro is assigned to the channels 1,2,5, and 6.
Waves that you added using the Add New Wave
 button can also be set to another channel configuration.
button can also be set to another channel configuration. - Show Spectral Envelope
-
Allows you to show/hide the spectral envelope, a smoothed curve of the harmonics’ levels which serves as a base reference curve for the formant filter.
- Formant Resolution
-
Allows you to specify how closely you want the envelope to follow the levels across the spectrum. Higher values result in a smoother curve and less pronounced formants. Lower values cause the curve to follow the levels more directly, resulting in a more detailed formant curve.
- Maximum Frequency
-
Allows you to limit the wavetable playback to the frequency range that is effectively used in the wave. This way, it is not necessary to compute the full spectrum, which can reduce the required processing power. The setting can be adjusted for each wave individually.
When you reduce this parameter, the number of editable harmonics in the spectrum view is adjusted accordingly.
Phase Spectrum Editing
You can use the Draw Tool to edit the phase spectrum of a wave in the same way as you edit the level of the harmonics. However, this editing method is quite abstract. While it is relatively easy to predict the effects of increasing or decreasing the level of a harmonic, it is much harder to do so with regard to the effects of changing the phase. In most cases, the phases of the harmonics must transition smoothly from one wave to the next. In situations where this is difficult to achieve, you can copy and paste the phase spectrum from one wave to another or to all waves within a wavetable. This way, phase alignment becomes much easier, and you only have to adjust the level transitions between the waves. As an alternative to selecting the phase spectrum of a wave, you can also randomize the phase spectrum.
Context Menu

- Select All
-
Selects all harmonics.
- Deselect All
-
Deselects all harmonics.
- Invert Selection
-
Selects all harmonics that were previously not selected, and deselects all harmonics that were previously selected.
- Copy Phase
-
Copies the phase spectrum of the focused wave to the clipboard.
- Paste Phase
-
Pastes the phase spectrum from the clipboard to the selected waves.
- Random Phase
-
Randomizes the phase spectrum of the selected waves. The same random phase spectrum is applied to all channels, to maintain a correlated stereo or surround image.