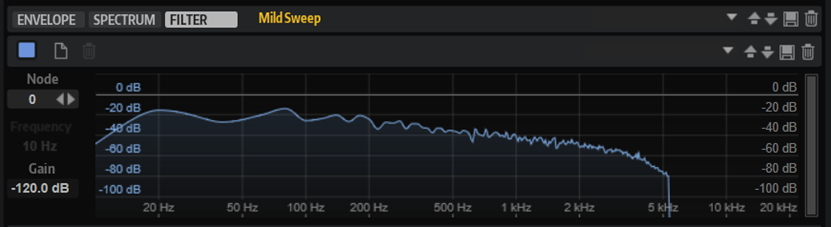
Filter Tab
The Filter tab allows you to edit the spectral filter that is integrated in the wavetable oscillator and to apply this filter to all or to specific waves of the wavetable.
You can apply individual filters to each wave or apply the same filter to the entire wavetable.
- Filter On/Off
-
Activates/Deactivates the spectral filter.
- Create Filter
-
Creates a filter for the selected waves.
If you create a filter for one wave of the wavetable, this filter is applied to all waves.
Example
-
To apply filters exclusively to specific waves, select the waves, click Create Filter, and edit the filter. Waves without an own filter are played back with blended filters of the preceding and subsequent waves.
-
To apply one filter to the entire wavetable, select a single wave, click Create Filter, and edit the filter. If no filter is specified for any of the other waves in the wavetable, this filter affects all waves.
- Delete Filter
-
Deletes the filter.
- Node
-
Displays the selected node. You can use the arrow buttons to switch between nodes.
- Frequency
-
Sets the frequency of the selected node.
- Gain
-
Sets the gain of the selected node.
- dB Range
-
The scrollbar on the right side allows you to define the dB range in which the filter curve can be adjusted. By default, it is set to the maximum range of +20 dB to 120 dB. This allows you to limit the range, for example, if you want to make very subtle adjustments within a range of +/-12 dB.

Drag the upper or lower edge to change the maximum value or the minimum value of the range. When the range is limited, you can also drag the middle of the scrollbar to change both at the same time.
Context Menu
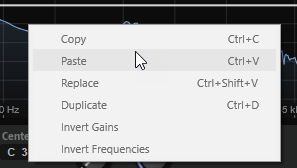
- Copy
-
Copies the selected nodes to the clipboard.
- Paste
-
Pastes the copied nodes at the insert position.
- Replace
-
Replaces the selected nodes with the nodes from the clipboard.
- Duplicate
-
Duplicates the selected nodes.
- Invert Gains
-
Flips the Gain values of the nodes around the vertical center of the selection. This way, you can turn a filter bump into a filter dip, for example.
- Invert Frequencies
-
Flips the nodes around the horizontal center of the selection. This way, you can mirror the symmetry of an asymmetrical filter shape, for example, to turn a low-pass filter into a high-pass filter.